Magento 2 MySQL optimization is the step you should start from on the way to your website performance enhancement. Working with this complex e-commerce platform, you know that it has a robust event logging system, which stores collected customer info in Magento 2 module version database tables.
Now imagine that you run a huge store and all the logs haven’t been cleaned up for ages. Will this influence your website performance? A definite yes, we think.
Back up your database before launching any optimization process.
→ There's a lot to be said about Magento 2 website optimization. But we have one answer to all Google Page Speed Insights suggestions - M2 Google Page Speed Optimizer: minifies/merges JS, CSS, HTML, implements lazy loading, supports WebP images, speeds up loading on mobiles and desktops. To learn more about Magento 2 database optimization, check out this guide.
In this post, we’ll cover how to run Magento 2 database optimization in 3 simple ways.
Magento 2 MySQL Optimization Fact-Checking
Unlike Magento 1, where System and Exception log files were disabled by default and needed manual enablement via admin, Magento 2 has them enabled by default. So, you don’t need to do any additional actions in Magento 2 to make them work.
Today, we’ll be talking mostly about the log type that saves logs of any events related to customers’ activities. The data is saved in Magento 2 database tables we list below:
log_customer
log_visitor
log_visitor_info
log_visitor_online
log_summary
log_summary_type
log_url
log_url_info
log_quote
Index_event
report_event
report_viewed_product_index
report_compared_product_index
catalog_compare_item
dataflow_batch_export
dataflow_batch_import
As you may have guessed, the Magento 2 user tables contain lots of useful info like a customer's login/out date and time, the URLs they visited as a part of a session, the products they compared, the quoMySQL Message Queue Cleanuptes they made, their actions in store, in general, and so on.
All this data accumulates and hampers your Magento 2 if not cleaned timely. Thus, the bigger the store, the more unnecessary info overloads your website. So, here are three ways to solve this.
#1 Magento 2 Database Optimization: Log Cleaning and Flat Catalogs via Admin Panel
This is the simplest Magento 2 database optimization solution for non-technical store owners who don’t want to interact with coding. Here’s how it works:
Step 1: Log in to your admin panel.
Step 2: Go to Stores > Configuration.
Step 3: Go to the left sidebar, find the Advanced menu, and click on System.
Step 4: Choose the MySQL Message Queue Cleanup and set up a desired automatic log cleaning frequency, or leave the default ones like on the screenshot below:
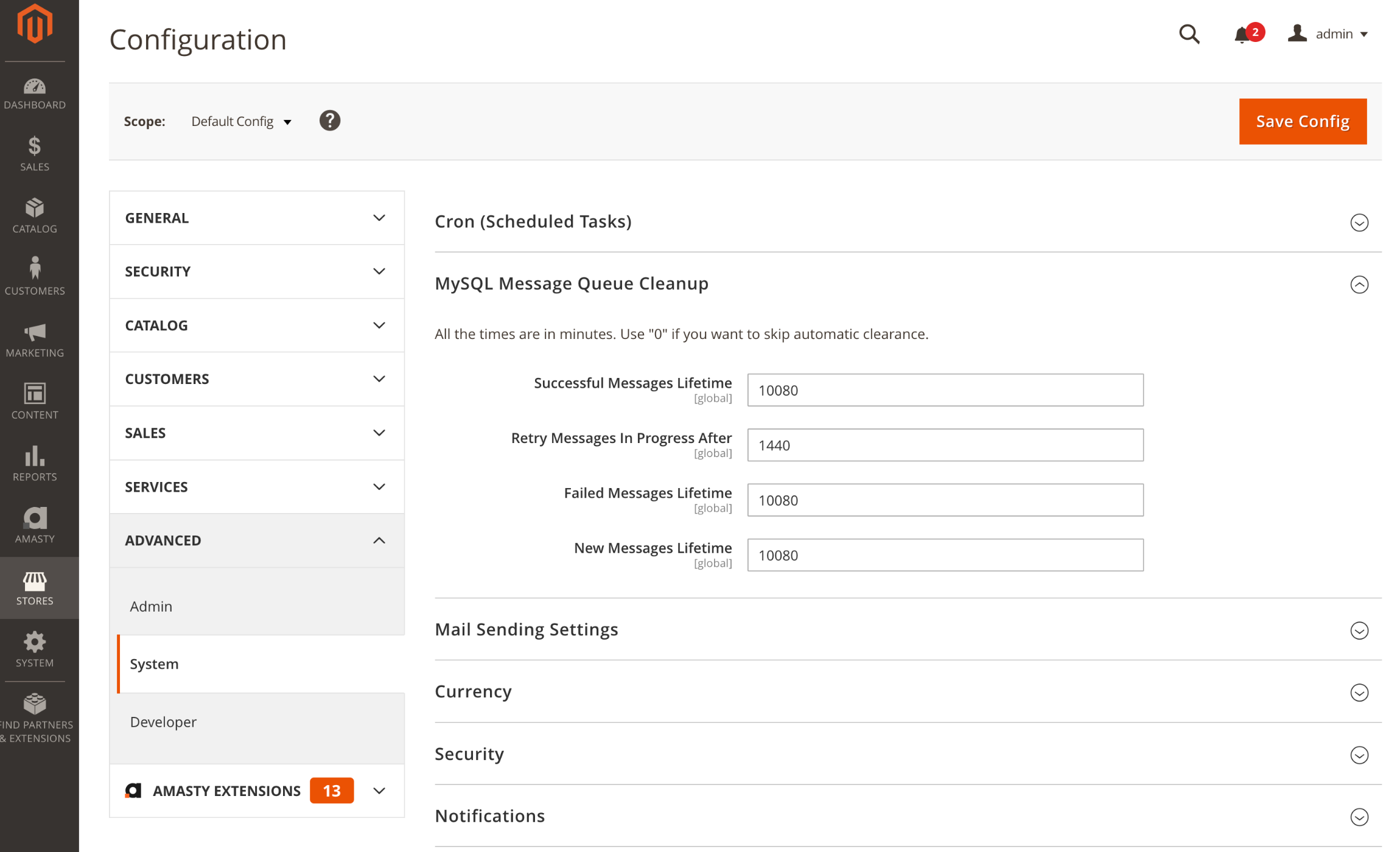
Step 5: Click on Save Config.
#2 Cleaning Magento Database Logs: Use MySQL Client or CLI
Via MySQL Client
For users familiar with manual Magento 2 database management, this approach offers the most efficient way to clear logs. This method consolidates the data in the tables, reducing the size of the database by up to 95% and improving query times.
Step 1: Enter the phpMyAdmin panel from your hosting control panel.
Step 2: Enable the checkboxes for the next tables with logs:
- Note: This data may be used in some important reports for your Magento 2 website. And if it is, then don’t clear the corresponding log.
- Note 2: Be careful with clearing the catalog_compare_item table, as your clients will lose the comparison data. Make sure to discard only the data that is old, so as not to affect the user experience and interaction with the website.
log_customer
log_visitor
log_visitor_info
log_visitor_online
log_summary
log_summary_type
log_url
log_url_info
log_quote
Index_event
report_event
report_viewed_product_index
report_compared_product_index
catalog_compare_item
dataflow_batch_export
dataflow_batch_import
+ enterprise_logging_event and enterprise_logging_event_changes if use EE.
Step 3: Go to the action drop-down With Selected menu at the bottom of the page and choose Empty. Then click Yes in the appeared confirmation page. Thus, you’ve just truncated the selected tables.
Step 4: Now go to the top of the page and click on the Structure tab. Tick the same tables you’ve just truncated and under the With Selected list click on Optimize. That’s it.
#3 Cleaning Magento Database Logs: Use shell/log.php
You can make Magento 2 database cleanup through the log.php file in Magento /shell. It can be run both manually and via a cron job.
If running the cleaning manually, then...
Step 1: Go to the root directory and use the command: php -f shell/log.php clean
Step 2: In order to specify the number of days of logging history to be saved, use the ‘--days’ line:
$ php -f shell/log.php help
Usage: php -f log.php -- [options]
php -f log.php -- clean --days 1
clean Clean Logs
--days <days> Save log, days. (Minimum 1 day, if defined - ignoring system value)
status Display statistics per log tables
help This help
Step 3: See the results php -f shell/log.php status. It may take some time to process your request, it depends on how long ago you did it last time.
Note that we can’t remove data from all the log tables using this method, as it removes the visitors’ chosen data by their IDs only.
Disable Magento logging
If you (a) don’t want to decrease your Magento 2 performance, (b) don’t need the customers’ data gathered by Magento, (c) don’t want to check the Magento 2 alter table logs statuses all the time, you can disable logging to the database.
By the way, if you stop logging from the Magento 2 admin panel, it doesn’t solve the problem fully. To stop this completely, follow the next steps.
Step 1: Open the app/etc/local.xml file;
Step 2: Paste the next patch before the tag:
<frontend>
<events>
<controller_action_predispatch>
<observers><log><type>disabled</type></log></observers>
</controller_action_predispatch>
<controller_action_postdispatch>
<observers><log><type>disabled</type></log></observers>
</controller_action_postdispatch>
<customer_login>
<observers><log><type>disabled</type></log></observers>
</customer_login>
<customer_logout>
<observers><log><type>disabled</type></log></observers>
</customer_logout>
<sales_quote_save_after>
<observers><log><type>disabled</type></log></observers>
</sales_quote_save_after>
<checkout_quote_destroy>
<observers><log><type>disabled</type></log></observers>
</checkout_quote_destroy>
</events>
</frontend>
And save the local.xml file.
Step 3: Navigate to System>Configuration>Advanced>Disable Modules Output and choose Disable for Mage_Log:
Step 4: Flush your Magento 2 Cache.
You may even turn to more radical methods and say, hack the core code.
Bonus Info: Flat Catalogs
Magento 2 stores product and category data in EAV (Entity-Attribute-Value) tables, which allows flexibility but can make queries slower when you have many products or attributes.
A flat catalog takes all product or category data and stores it in a single, flat table. This reduces joins in SQL queries and can speed up catalog performance. Still, this option may not suit every Magento 2 store.
Reasons to use a flat catalog

Improved frontend performance. For stores with thousands of products, flat tables can significantly speed up category pages, layered navigation, and search queries, as well as reduce complex EAV joins, making queries faster.
Better performance with layered navigation. Layered navigation relies heavily on product attributes. With flat tables, filtering is faster because the data is pre-joined and stored in a single table.
Simpler SQL Queries. Flat tables are easier to query for developers, especially if you build custom reports or modules that fetch product data.
Reasons not to use flat catalog
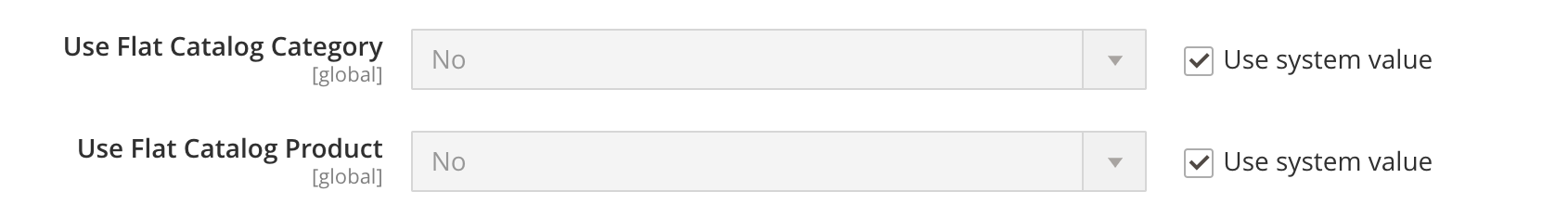
Data update overhead. Every time you add or update a product/attribute, Magento 2 must rebuild the flat tables. For stores with frequent updates, this can slow down admin operations or require scheduled reindexing.
Limited flexibility. Flat tables don’t fully support complex EAV features, like custom product attributes and multi-store or multi-language setups. Some third-party modules may not fully work with flat tables.
Newer versions of Magento. Since Magento 2.1+, flat tables are less necessary because a) catalog indexers and database query optimization have improved, and b) many Magento 2 stores don’t see a significant speed gain from enabling flat catalogs.
Maintenance complexity. Flat tables can create extra maintenance tasks like reindexing manually or via cron jobs, or handling potential sync issues between flat tables and EAV tables.
That said, flat catalogs may be good for Magento 2 MySQL optimization if the store is pretty big with slow EAV queries. Anyway, monitor the performance to take measures on time.
Sum-up
Remember that Magento 2 MySQL optimization and database log cleaning are a must-have for good performance of your website. Besides, you can always migrate from MySQL to any other database engine, say, it can be Magento 2 and MariaDB, Amazon Aurora, Magento Percona or anything else. The only thing to remember is that if you haven’t configured automatic deletion of logs, do not forget to do this manually.
Still have questions?
Feel free to pose them below! Or check our server configuration service.
P.S. Special thanks to Dmitry Smolik and Alexander Seravin for the expertise that helped us bring this post to life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Use indexing: Properly indexing columns that are frequently queried can speed up search operations.
Optimize queries: Review and optimize slow queries in MySQL logs.
Increase cache size: Increase the query cache and buffer pool size in MySQL settings for better performance.
Use proper data types: Ensure that the data types of your tables are correctly defined to reduce storage and improve speed.
Disable unnecessary features: Disable unused features like the query cache if not needed.
Enable Full Page Cache. Use Varnish or Redis for caching to reduce page load time.
Optimize images. Compress images and use the right formats (WebP, etc.).
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN). Offload static content like images and CSS/JS files to reduce server load.
Enable and configure Redis. Use Redis for both cache and session storage to improve performance.
Minify CSS and JavaScript. Minify and bundle CSS and JS files to reduce page load time.
Actual versions of Magento 2 support MySQL 8.0 and MySQL 8.4. These MySQL versions ensure better performance and support for modern features (like JSON data types). Also, check if you're using InnoDB as the default storage engine for better reliability and performance.
Disabling the indexer in Magento 2 is not recommended for live sites, as it will affect performance. Still, if you need it for some reason, you can run this CLI command:
bin/magento indexer:set-mode manual
This will prevent Magento from automatically reindexing whenever a change is made to product data, categories, etc.
You can manually trigger reindexing with:
bin/magento indexer:reindex


















